1. Background
Hot-melt adhesives are solid at room temperature. When heated to a certain temperature, they melt into a viscous liquid. After cooling to room temperature, they become solid again and have a strong bonding effect, so people call it hot-melt. (type) adhesive (referred to as hot melt adhesive). Because hot melt adhesive has the advantages of fast bonding speed, non-toxicity, simple bonding process, good bonding strength and flexibility, etc., it has been widely used in book binding, packaging sealing, shoemaking, textiles, etc. Applications, and in recent years there are new developments in terms of variety and performance. Hot melt polyurethane adhesive is one of the more important ones.
2. Polyurethane hot melt adhesive
Polyurethane hot melt adhesives can be divided into two categories: one is thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer hot melt adhesive, and the other is reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive;
2.1 Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer hot melt adhesive
Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer hot melt adhesive is made of polyurethane elastomer with a molecular weight of more than 15,000, plasticizer, tackifying resin, accelerator, lubricant, filler, etc. Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer hot melt adhesives react linear or slightly branched polymer diols, low molecular weight chain extenders and isocyanates to form chain-like polymer compound carbamates, namely Polyurethane. When in use, it is heated to a certain temperature, melted and coated on the surface of the substrate, and then solidified by cooling. The curing process mainly uses the hydrogen bond in the composition to cause physical crosslinking, which has excellent toughness and bonding strength; but the degree of crosslinking is low. , poor heat resistance and solvent resistance.
2.2 Reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive
Reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive is also called reactive moisture curing polyurethane hot melt adhesive. This type of adhesive is divided into closed type and moisture curing hot melt type. This type of adhesive is based on NCO-terminated prepolymer, together with thermoplastic resins and tackifying resins that do not react with isocyanate groups, as well as additives such as antioxidants, catalysts, fillers, etc., to ensure that the products have a longer pot life and storage. Expect. The main component of the reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive is an isocyanate-terminated polyurethane prepolymer synthesized from polyester or polyether polyol and polyisocyanate. After the prepolymer melts and sizing, it solidifies quickly and has a certain initial bonding strength. During the further post-curing process, the moisture gradually diffuses into the adhesive layer and reacts with the isocyanate group at the end of the prepolymer to form urea and biscondensate. Urea and allophanate form a cross-linked macromolecular network structure, thus exhibiting ideal heat and solvent resistance. Reactive polyurethane hot melt adhesive has good bonding ability to different substrates such as rubber, plastic, glass, metal, leather, wood, fabric, etc., and also has a relatively high cohesive strength; it is widely used in automotive structures, zero Parts, textile and footwear industry, food packaging industry, wood processing and furniture industry, electronics and electrical appliances industry and many other fields.

2.2.1 Curing principle:
Reactive moisture-curing polyurethane hot melt adhesive mainly reacts with polyether or polyester polyol and diisocyanate to form a terminal isocyanate (-NCO) prepolymer. When the -NCO content reaches a certain set value, adding It is formulated with NCO-reactive thermoplastic resin, tackifying resin, filler, antioxidant, catalyst and other additives. When in use, heat and melt PUR and apply it to the surface of the adhered material, then stick the two coated objects together, and after cooling, the adhesive layer will condense to play a bonding role; then use the moisture in the environment or the moisture in the adhered material and Other active hydrogen-containing compounds react with an NCO group to extend the chain to form a cross-linked polymer with high cohesion and adhesion, which further plays the role of adhesion. The main reactions of an NCO group in PUR with water or other active hydrogen-containing compounds are shown below.
OCN-R-NCO+H2O→-RNHCOOH
-NCO+-NHCOO-→-N(CONH-)COO-
-NCO+-NHCONH-→-NC(CONH-)ONH-
Due to the high polarity of the urethane chains (-NHCOO-) and urea chains (-NHCONH-) generated in the reaction, they constitute the rigid chains of the polyurethane (PU) molecular structure, so that the adhesive has a higher Strength and heat resistance, and the soft segment structure itself has strong low temperature resistance. Therefore, PUR not only has the characteristics of hot melt adhesive solvent-free, high initial viscosity and fast positioning, but also has the water and temperature resistance of reactive adhesives. Creep, moisture and media resistance properties. It can be seen that PUR can be used not only as an adhesive, but also as a sealant, and can bond porous materials (such as foam plastics, ceramics, wood and fabrics, etc.) foil, glass and rubber, etc.). At the same time, it has a relatively high cohesive strength for the bonding between porous materials and materials with smooth surfaces, and the ratio of different raw materials can be adjusted according to needs to obtain adhesives from flexibility to rigidity. It is often used in automobiles and bookbinding. , textiles, shoemaking, wood processing, furniture, construction, electronics and electrical appliances and other fields.
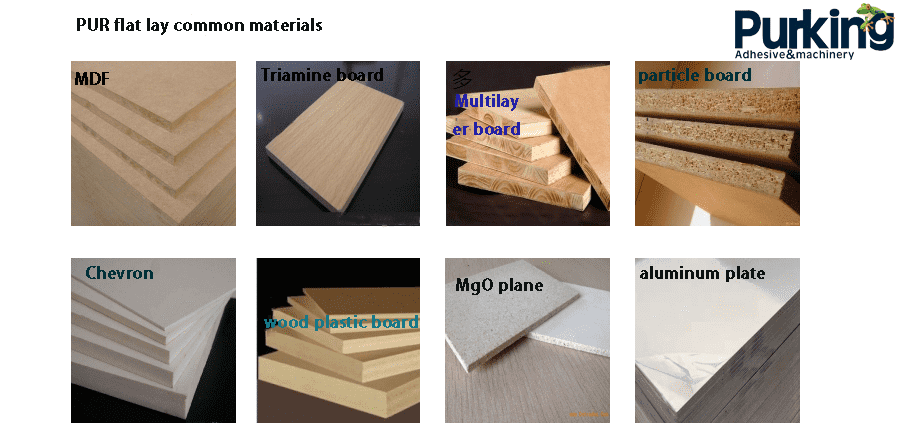

3. Common components of polyurethane hot melt adhesive
Polyurethane hot melt adhesive is mainly composed of polymer matrix, plasticizer, tackifying resin, accelerator, catalyst, lubricant, filler, additive and so on.
3.1 Polymer matrix:
Polyurethane is white irregular spherical or columnar particles, which are divided into two categories: polyester type and polyether type. Polyester polyols are commonly used to polymerize with diisocyanates. Commonly used raw materials are isocyanates (TDI, MDI, HDI, IPDI, etc.), polyester polyols (generated by the reaction of polyols and polyacids, commonly used polyacids are adipic acid, commonly used polyols are 1,2-butanediol, ethyl Diol, etc.), polyether polyols (commonly used are PPG, POP, PTMEG, etc.).
3.2 Tackifier
Improve bonding strength, reduce cost, improve handling performance, improve impact strength and peel strength, adjust heat-resistant temperature and exposure time. Commonly used tackifiers: 1) Rosin and its derivatives: rosin; hydrogenated rosin; polymerized rosin; disproportionated rosin; glycerol rosin ester; 2) terpene and modified terpene resin; 3) petroleum resin: C5 petroleum resin; C9 Petroleum resin; C5/C9 petroleum copolymer resin; aliphatic petroleum resin.
3.3 Plasticizer
Plasticizers can reduce the glass transition temperature and melting temperature of polymer compounds, improve the brittleness of the adhesive layer, and improve the fluidity of the molten material. Requirements: good compatibility, durability, stability, no reaction with the main body, light color. Often high boiling point, difficult to volatile liquid. Addition amount: no more than 10%. Dioctyl phthalate and trioctyl trimellitate, etc.
3.4 Viscosity modifiers
In order to improve the melt fluidity of hot melt adhesives, some viscosity regulators are often added to reduce the melt viscosity of hot melt adhesives, improve fluidity, shorten exposure time, improve creep resistance, flexibility and melting speed, and reduce pumping. Silk phenomenon, to prevent self-adhesive rubber and other effects. Commonly used viscosity modifiers are some waxes (including paraffin wax, microcrystalline wax and synthetic wax).
3.5 Antioxidants
As an antioxidant, it should meet the following requirements: good compatibility with the adhesive, preferably compatibility; good performance in inhibiting and delaying oxidation; not affecting the process and physical and mechanical properties of the adhesive; stable in storage, and not causing discoloration and separation of the adhesive layer, gel, deterioration, etc.
3.6 filler
A filler is a filling material, also known as a filler, which is a solid material that does not react chemically with the main body. It can reduce shrinkage, prevent self-adhesion, reduce costs and prolong the operation time of glue. Addition amount: usually about 20%. Talc powder, barite powder, mica powder, calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, asbestos powder, titanium dioxide, asbestos powder, aluminum, iron powder, corundum powder, corundum, etc.
3.7 Catalyst
Increase or control cure speed. Commonly used catalysts: 1) tertiary amine, triethyleneamine [N-(CH2CH2)3-N] (good effect), methyldiethanolamine, triethanolamine, etc.; 2) organometallic salts: dibutyltin dilaurate, cyclic Cobalt alkanoate, zinc naphthenate, lead naphthenate, lead zincate; 3) Organic phosphorus: tributyl phosphorus, triethyl phosphorus, etc.
Organotin catalysts are selective for the reaction between isocyanate and water or alcohol. Tin can accelerate the reaction of -NCO/-OH, but has little catalytic effect on the reaction of -NCO/H2O; while tertiary amine compounds can simultaneously catalyze isocyanate Reacts with water or alcohols. In practical applications, two types of catalysts are usually used in combination to achieve a synergistic effect
3.8 Chain extender
Chain extender is a functional additive commonly used in the preparation of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers. It is characterized by small molecular weight, short chain links, and active reactivity. Generally, it is an amine or alcohol composed of 2-4 functional groups. class of compounds. Usually BDO is used as chain extender.
3.9 Additives
Additives include flame retardants, antioxidants, UV inhibitors, desiccants, colorants, coupling agents, etc.
4. Polyurethane hot melt adhesive reference formula (for reference only)
|
Composition
|
Content
|
Composition Description
|
|
Polyurethane Prepolymer
|
50-60%
|
Polymer Matrix
|
|
SU-120
|
5-15%
|
Tackifier
|
|
Antioxidant 1010
|
0.2-1%
|
Antioxidant
|
|
Chlorinated Paraffin
|
3-6%
|
Plasticizer
|
|
Calcium Oxide
|
15-20%
|
Filler
|
|
AV5012
|
6-10%
|
viscosity regulator
|
|
Dibutyltin Dilaurate
|
0-1%
|
Catalyst
|
|
UV Inhibitor
|
0-1%
|
Antioxidant
|
Thank you so much for watching to the end!
I don't know if this article is helpful to you. If you have any questions, you can contact us, Get to know us, and contact us.
 English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Sundanese
Sundanese  Yoruba
Yoruba  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Slovensky jazyk
Slovensky jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик