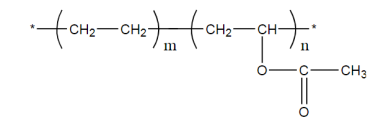Hot-melt adhesive is a kind of solid adhesive after melting and mixing with thermoplastic resin as the base material, adding various tackifiers, antioxidants and other auxiliary materials. It has the advantages of no solvent, convenient synthesis, short curing time, wide bonding range, convenient storage and transportation, and environmental protection, so it has achieved rapid development.
Applications in various industries have also flourished. Among them, EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) hot melt adhesive has good adhesion to all materials due to its excellent bonding performance, and has good adhesive layer toughness, weather resistance, and heat resistance. , low melt viscosity, low price and other advantages, so it has become a type of hot melt adhesive with fast development, wide application and large consumption in hot melt adhesives.
EVA hot melt adhesive is usually composed of EVA resin, tackifying resin, viscosity regulator, antioxidant, filler and so on.
EVA resin
EVA resin is an essential matrix resin in the composition of EVA hot melt adhesive, which determines the cohesive strength, flexibility and bonding strength of the hot melt adhesive to the substrate. EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) is made by bulk polymerization of ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer at a certain temperature and high pressure (the structural formula is shown in Figure 1). Due to the introduction of vinyl acetate monomer in the molecular chain, the degree of branching of the polymer is increased, thereby reducing the crystallinity, improving flexibility, impact resistance, filler compatibility and heat sealing, and the resin is in a wide range It has good flexibility, impact strength, environmental stress cracking resistance, good optical properties, low temperature resistance and non-toxic characteristics in a certain temperature range.
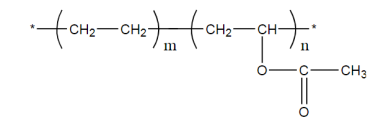
Figure 1 The structural formula of EVA
The proportion and content of ethylene and vinyl acetate (VA) monomers in EVA resin have a great influence on the performance of the resin. Usually, the VA content of EVA resin used in EVA hot melt adhesives is between 18-40%, and the VA content increases. The toughness, impact resistance, softness, stress crack resistance, viscosity, heat sealing and repeated bending of the resin at low temperature are increased, the peel strength of the adhesive is improved, and the elasticity of the rubber is increased, but the strength, hardness, melting point and heat distortion temperature also decreased. Therefore, according to the different needs of hot melt adhesives, EVA resins with different VA contents are usually selected for use alone or in combination.
Tackifying resin
Tackifying resin refers to a class of small molecular polymers that can increase the viscosity of rubber materials. The relative molecular weight is usually below 10,000, the softening point is between 60°C and 150°C, and the glass transition temperature is higher than room temperature. It has certain thermoplasticity but The mechanical properties are extremely low. Tackifying resins are usually not used alone, and are mainly used as low-molecular modifiers in hot-melt adhesives, polymer coatings, and rubber. Among them, tackifying resins are most widely used in the field of hot melt adhesives, and the annual consumption of tackifying resins for hot melt adhesives accounts for more than 60% of its total production in the world.
The tackifying resins commonly used in EVA hot melt adhesives are mainly divided into three types: rosin resins, terpene resins and petroleum resins. The main component of rosin is abietic acid (structure shown in Figure 2), which accounts for more than 90% of the total amount, and there are also a small amount of fatty acids and neutral substances. The structure of rosin acid contains double bond and carboxyl group, has strong reactivity, is unstable under light, heat and oxygen conditions, shows poor aging resistance, poor weather resistance, and is prone to discoloration and other phenomena. Therefore, on the basis of rosin, various derivatives such as hydrogenated rosin, disproportionated rosin, polymerized rosin, esterified rosin and maleated rosin are derived (the structure is shown in Figure 2). These derivatives can not only improve the instability of rosin, but also endow rosin with more excellent properties, and are widely used in tackifying resins.
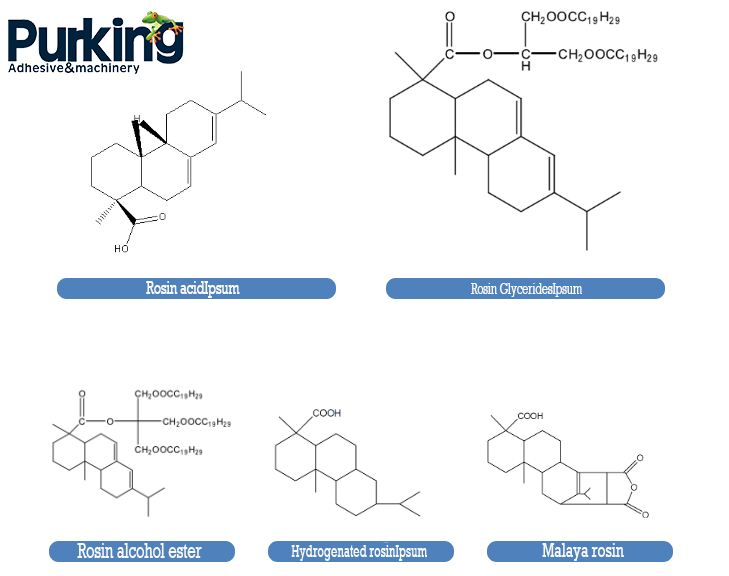
Figure 2 Structural formulas of rosin and its derivatives
Terpene resin, also known as pinene resin. It is mainly a series of linear polymers from liquid to solid obtained by cationic polymerization of α-pinene or β-pinene of turpentine under the action of Freckers catalyst. And it has good compatibility with various synthetic substances. Soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons and vegetable oils.
Petroleum resin is a compound obtained by cationic polymerization of aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbons, which are by-products of cracked petroleum. Petroleum resins include pure C5 petroleum resins, C9 petroleum resins and C5/C9 copolymerized petroleum resins. The overall performance of petroleum resin is slightly worse than other resins, but the price is more reasonable. The modified C5 petroleum resin not only improves the adhesion and softening point, but also greatly enhances its polarity due to the introduction of polar groups.
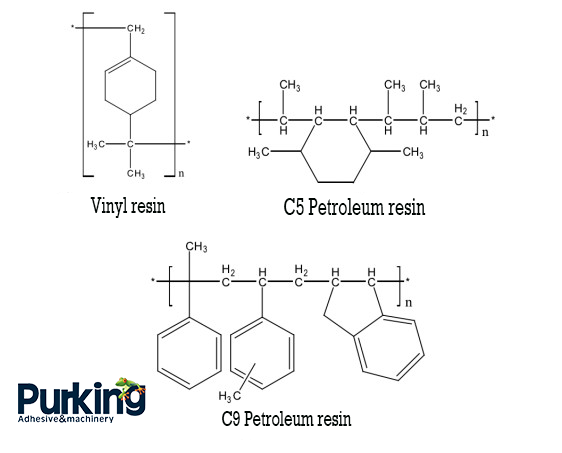
Figure 3 Structural formula of terpene resin and petroleum resin
viscosity modifier
Viscosity modifier, as the name suggests, is an additive to adjust the viscosity of polymers. It is often used in EVA hot melt adhesives to reduce melt viscosity, improve colloidal fluidity, shorten open time and reduce stringing. The dosage generally does not exceed 25% in hot melt adhesive.
Commonly used viscosity modifiers are usually waxes. There are many types of waxes, but not all waxes are suitable for hot melt adhesives. The esters and unsaturated bonds in animal and vegetable waxes will affect the resistance of hot melt adhesives. Aging and thermal stability, so the waxes used for preparing hot melt adhesives are mainly mineral waxes and synthetic waxes, such as: microcrystalline wax, paraffin wax, polyethylene wax and Fischer-Tropsch wax.
The carbon atom distribution of paraffin in mineral wax is relatively narrow, and it exists almost in the form of a straight chain. It has good stability and low melt viscosity, but the softening point and melting point of paraffin are too low, which will directly affect the thermal properties of hot melt adhesives; microcrystalline Compared with paraffin wax, the distribution of carbon atoms is wider and the molecular weight is higher. In addition to the straight chain structure, there are also branched chain and ring structures in the microcrystalline wax molecular chain. The molecular crystallinity is low and there are amorphous regions. Microcrystalline wax has Excellent low temperature resistance, which has a great influence on the glass transition temperature of hot melt adhesives, suitable for the preparation of low temperature resistant hot melt adhesives.
Polyethylene wax and Fischer-Tropsch wax in synthetic wax are both high crystalline waxes, which contain a large amount of n-alkane structure, and have the characteristics of high hardness, high melt viscosity, low temperature resistance, high melting point and softening point, and are generally suitable for high temperature resistance, Preparation of fast-curing hot melt adhesives.
antioxidant
Antioxidants are a class of chemical additives commonly used in polymers, which can delay and prevent the oxidation of polymers. A small amount of antioxidants are generally added to hot melt adhesives, mainly to prevent deterioration and decrease in bond strength caused by oxidative decomposition of hot melt adhesives during high temperature preparation and construction. Commonly used antioxidants include antioxidants BHH264, 1010, 1135, 168, etc.
filler
Adding fillers can reduce the cost of hot melt adhesives and improve some properties of hot melt adhesives. Adding fillers to EVA hot melt adhesive can improve the heat resistance of the colloid, reduce the shrinkage of the rubber material, and control the fluidity of the rubber material. Commonly used fillers include clay, white carbon black talcum powder, titanium dioxide, barium sulfate, etc.
At present, hot melt adhesives are mainly used in packaging, wood, book binding, clothing, automobile, construction and other industries. In wood processing, it is mostly used for edge banding of furniture. In the packaging industry, it can be used in cardboard and cardboard boxes, cement bags, stickers, food packaging, protective packaging, packaging container sealing and other fields. In the clothing industry, it is often used as an adhesive for hot-melt adhesive interlinings. In addition, it can also be used in the manufacture of televisions, air conditioners, refrigerators and other electrical appliances, as well as in the shoe industry, PET blow molding bottles and polyolefin-based cups, SO non-woven composite cement packaging bags, the connection of carpet backing, the coiling of cigarette filters, tearing strips of outer packaging, sealing of cable joints, oil pipeline anticorrosion and other fields.

Purking has rich research experience in the analysis of EVA hot melt adhesives. It has built a powerful spectral library. Through analysis and testing, it can determine the components and proportions of EVA resins, tackifying resins, viscosity modifiers, antioxidants and other additives, and compare and analyze product differences. , to help develop new products and improve product performance.
 English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Català
Català  שפה עברית
שפה עברית  Cymraeg
Cymraeg  Galego
Galego  Latviešu
Latviešu  icelandic
icelandic  ייִדיש
ייִדיש  беларускі
беларускі  Hrvatski
Hrvatski  Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen  Shqiptar
Shqiptar  Malti
Malti  lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili  አማርኛ
አማርኛ  Bosanski
Bosanski  Frysk
Frysk  ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ  ქართული
ქართული  ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી  Hausa
Hausa  Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили  ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ  Corsa
Corsa  Kurdî
Kurdî  മലയാളം
മലയാളം  Maori
Maori  Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл  Hmong
Hmong  IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa  Zulu
Zulu  Punjabi
Punjabi  پښتو
پښتو  Chichewa
Chichewa  Samoa
Samoa  Sesotho
Sesotho  සිංහල
සිංහල  Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig  Cebuano
Cebuano  Somali
Somali  Тоҷикӣ
Тоҷикӣ  O'zbek
O'zbek  Hawaiian
Hawaiian  سنڌي
سنڌي  Shinra
Shinra  Հայերեն
Հայերեն  Igbo
Igbo  Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch  Malagasy
Malagasy  Sundanese
Sundanese  Yoruba
Yoruba  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Az?rbaycan
Az?rbaycan  Slovensky jazyk
Slovensky jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик